Quenching- and Deformation Dilatometer
A so-called quench dilatometer is suitable for the determination of phase transformations under industrial relevant heating and cooling conditions. Three devices (TA Instruments DIL805 A/D/T and DIL805 A) are available at the department. The former is equipped with a tensile/compression deformation unit, which is used to determine the deformation behaviour of the tested material. The specimen is inductively heated by a water-cooled double-walled coil and cooled through the inlet of gas into the chamber. The change in length is recorded as a function of time or temperature or the degree of deformation. From this, for example, continuous and isothermal time-temperature transformation diagrams (TTT) as well as deformation-time-temperature transformation diagrams (DTTT) can be generated.
Main applications: Determination of thermal expansion coefficients, kinetics of phase transformations, generation of TTT, TTA and DTTT diagrams, generation of flow curves, simulation of heat treatments and deformation processes.
Technical data:
Quenching Dilatometer:
- Temperature range: 20°C to 1500°C, cryogenic temperatures -200°C to 1100°C
- Heating: inductive
- Atmosphere: nitrogen, helium, vacuum, air
- Heating rate: max. 4000 K/s
- Quenching rate: max. 2500 K/s
- Resolution: 50 nm, 0,05°C
- Specimen geometry: round samples, length 10 mm, diameter 3-5 mm, Cryogenic samples only with hollow round samples, diameter 4-5 mm
Deformation Dilatometer:
- Temperature range: 20°C - 1500°C
- Heating: inductive
- Atmosphere: nitrogen, helium, vacuum, air
- Heating rate: max. 100 K/s
- Quenching rate: max. 100 K/s
- Resolution: 50 nm, 0,05°C
- Specimen geometry: round samples, length 10 mm, diameter 3-5 mm, round and and flat tensile samples
- Forming speed: compression: 0,001 to 20 s-1, tension: 0,001 to 1 s-1
- Degree of deformation: 0,01 to 1,2
- Compressive force: max. 20 kN
- Tractive force: max. 10 kN
Atom probe tomography


For the characterization of materials with near-atomic resolution, Atom Probe Tomography (APT) is of special interest. For such investigations, an atom probe of the type LEAP 5000 XR, as well as a LEAP 3000X HR from Cameca Inc. are available.
In atom probe tomography, a DC voltage of several kilovolts (5-15 kV) is applied to a tip with a tip radius of 20-50 nm. By means of a superimposed voltage or laser pulse, atoms are removed from the surface by the effect of field evaporation and accelerated onto a position-sensitive detector. The detector simultaneously records the time of flight as well as the positions of the arriving ions, enabling a 3D reconstruction of the ablated tip providing information about its chemical structure. Almost the entire periodic system can be resolved by the atom probe. By the use of a laser pulse, materials with poor electrical conductivity can also be analysed. Especially the UV laser (wavelength: 355 nm) of the LEAP 5000 XR enables investigations on of complex materials, ceramics and even geological materials.
Main applications: precipitation reactions, grain boundary segregation, chemical clustering, multifunctional thin films
Technical data:
LEAP 5000 XR:
- Temperature range: 20K to 100K
- Imaging gas: Neon, Helium, Argon
- Field of view: > 150 nm
- Mass resolution: FWHM > 1100
- Laser: UV (wavelength: 355 nm)
LEAP 3000x HR:
- Temperature range: 20K to 120K
- Image gas: Helium, Neon
- Field of View: < 200 nm
- Mass Resolution: FWHM ≤ 1100
- Laser: green (wavelength: 532 nm)
Differential Scanning Calorimetry and thermogravimetric analysis
Dynamic methods are particularly suitable for efficient determination of phase transformation temperatures. Two thermal analysis units (Setaram Setsys Evo 2400 and Setaram Labsys) are available at the department for this type of measurement. Both units are combinations of a dynamic differential calorimeter and a thermogravimeter. In differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), samples of known mass and suitable reference sample are subjected to a defined temperature program. Due to the thermal energy released or consumed during transformations in the sample, heat flow differences, which occur between the sample and the reference are recorded. This allows the determination of kinetics and temperature range of phase transformations, as well as reaction enthalpies and specific heat capacities. Thermogravimetry also detects changes in mass. Thus, for example, oxidation processes or decomposition reactions can be monitored.
Technical data:
Setsys Evo 2400:
- Measuring principle: dynamic differential calorimetry
- Temperature range: RT up to 1600°C/ after adaption up to 2400°C
- Heating- and cooling rate: 0,01 K/min - 100 K/min
- Atmosphere: argon, helium, synthetic air, vacuum
- Resolution: 0,4 µW
- Resolution scale: +-200 mg 0,3 µg, +-20 mg 0.03 µg
LabSys:
- Measuring principle: dynamic differential calorimetry
- Temperature range: RT up to 1600°C
- Heating- and cooling rate: 0,01 K/min - 100 K/min
- Atmosphere: argon, helium, synthetic air, vacuum
- Resolution: 0,4 µW
- Resolution Scale: +-1000 mg 0,2 µg, +-200 mg 0.02 µg
Focused Ion Beam

Site-specific sample preparation for transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and atom probe tomography (APT) requires specific preparation methods. At the Department is available the Dual Beam Focused Ion Beam Versa 3D device manufactured by FEI. This microscope incorporates a focused ion beam column (FIB) and a scanning electron microscope column (SEM). This duality offers the possibility of cross-section imaging during the ion beam does material milling/etching and/or deposition. In combination with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) enables elemental mapping, and in combination with Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) offers the possibility of crystallographic analysis.
Principal applications are: sample preparation for Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) investigations, sample preparation for Atom Probe Tomography (APT) and low-damage surface finishing
Technical data:
- Electron column: High-resolution field emission SEM column optimized for high-brightness / high-current
- Acceleration voltage (Electron column): 200V – 30kV
- Ion Column: High-current ion column with Ga liquid-metal ion source
- Acceleration voltage (Ion column): 0,5 – 30kV
- Detectors: SE, SI, BSE, STEM
- Gas Injektion System (GIS): Platin
- In situ Sample Lift-Out System: Omniprobe 100.7
High temperature laser confocal microscope
For in-situ observations of microstructural transformations, a Yonekura VL2000DX-SVF17SP high-temperature laser confocal microscope is available at the department. In the high-temperature chamber, which works according to the mirror furnace principle, the sample is heated by a halogen lamp and thus subjected to a predefined heat treatment. Any heat treatment up to a short-time temperature of 1800°C can be performed under argon atmosphere.
In this process, the microstructure becomes visible by thermal etching. A laser beam scans the sample surface, is reflected and detected by a light sensitive detector. A pre-set number of individual images, as well as a real-time video, are generated during the experiment. The device is suitable for investigating microstructural transformations during heating and cooling processes. Processes such as microstructural changes, grain coarsening or precipitation processes can be monitored in real time.
Technical data:
- Temperature range: 20°C - 1800°C (continuous temperature 1700°C)
- Heating system: mirror furnace principle with 1.5 kW halogen lamp
- Atmosphere: argon
- Heating and cooling rate: max. 6000 K/s (reasonable up to approx. 1000 K/min with helium as quenching gas)
- Maximum resolution: 0.14 µm
- Frame rate: 1 to 15 Hz
- Specimen geometry: standard cylinder specimen diameter 5mm, specimen height 1mm, polished with 3µm suspension, unetched
Ion milling systems Hitachi IM5000

Ion milling systems are widely used as instruments for preparing surfaces as well as cross-section samples for scanning electron microscopy (SEM), with applications to fields such as materials science and semiconductor research. The two types of ion-milling methods commonly used for SEM samples are flat milling and cross-section milling1)
Cross-section Milling
Used to produce wider, undistorted cross-sections without applying mechanical stress to the sample
Flat Milling
Used for removing surface layer artifacts and final polish after traditional mechanical polishing techniques.
Technical data:
- Ar ion gun, max. 8KV accelerating voltage
- Max. milling rate >1mm/hr for Si
- Cross-section and flat milling sample holder
- Max. sample size 20mm (cross-section), 50mm (flat milling)
3D Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope
The microscope is used for the characterisation of surface by recording and analysing 3 dimensional surface topographies. The laser beam scans the surface in x and y direction while a stepwise change of the focus point is achieved via the objective. The microscope is applied to analyse surface subjected to mechanical loading, e.g. after tribological tests, to measure 3 dimensional structure in microelectronics and nanoelectronics, to measure the thickness of opaque and transparent films as well as to determine the surface roughness.
Technical data:
- Device: Keyence VK-X1100
- Laser Wavelength: 404 nm
- Objectives: 5x, 10x, 20x, 50x and 150x
- Sample Stage: 100 mm x 100 mm
Laser ablation system microPREP™ PRO FEMTO
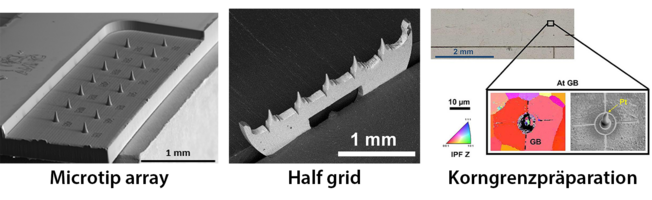
Our laser ablation system, the microPREP™ PRO FEMTO, offers a groundbreaking solution for precise material processing and sample preparation. Equipped with a state-of-the-art femtosecond laser, it enables material removal with micrometer precision while minimizing thermal effects on the material. This system facilitates the rapid and straightforward production of sample structures, such as microtip arrays [1] and half-grids [2], directly from the material, paving the way for revolutionary advancements in correlative microscopy [3].
Microtip arrays are coupons with 15 tips (radius <30 µm) that can be finalized for atom probe tomography (APT) in just a few steps using focused ion beam (FIB) technology. By eliminating the need for complex lift-out procedures, the system reduces effort and enhances the reliability of sample preparation. Half-grids, on the other hand, are semicircular structures that enable the simultaneous application of APT and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) on the exact same site, significantly simplifying correlative microscopy.
The combination of femtosecond laser technology and electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) allows for the precise preparation of site-specific features, such as grain boundaries. These capabilities make the microPREP™ PRO FEMTO an indispensable tool for cutting-edge materials research [3].
Highlights
- High-precision processing enabled by femtosecond laser technology
- Versatile for various sample structures and material types
- Optimized for advanced research needs, meeting the highest scientific standards
Technical Data:
- Wavelength: 515 nm
- Pulse duration: 230 fs
- Maximum power: 2.5 W
- Repetition rate: 60–1000 kHz
- Laser spot diameter: <10 µm
- Sample holders: X-Y stage and rotational sample holder
[1] M. Tkadletz, H. Waldl, M. Schiester, A. Lechner, G. Schusser, M. Krause, N. Schalk, Efficient preparation of microtip arrays for atom probe tomography using fs-laser processing, Ultramicroscopy 246 (2023). doi.org/10.1016/j.ultramic.2022.113672.
[2] M. Tkadletz, M. Schiester, H. Waldl, G. Schusser, M. Krause, N. Schalk, fs-laser preparation of half grid specimens for atom probe tomography and transmission electron microscopy, Mater Today Commun 39 (2024). doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2024.108672.
[3] J. Tang, O. Renk, M. Tkadletz, Site-specific femtosecond laser ablation: The pathway to high-throughput atom probe tomography characterization, Mater Charact (2024) 114618. doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2024.114618.
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy can be applied for the characterization of chemical bonds, phase changes or oxidation processes of construction and functional materials. The underlying Raman effect is based on the inelastic scattering of the light from a laser on the molecules within a sample. Thus, the chemical fingerprint of the sample can be characterized both laterally and depth resolved. Raman spectroscopy can be applied for a variety of material classes, for instance ceramics, polymers and semiconductors. Using the attached heating chamber allows to investigate the material behavior in-situ up to a temperature of 1500 °
Technical data:
- Device: Witec alpha300 R
- Wavelength of laser: 532 nm
- Lateral resolution: 250 nm
- Depth resolution: 1 µm
- Temperature regime: between room temperature and 1500 °C
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) Tescan Clara
SEM is widely used to study the microstructure and the chemical composition of a wide range of organic and inorganic materials. The electron beam, focused by an electromagnetic lens system, is scanning across the sample’s surface, which is located in an evacuated specimen chamber. Due to the interaction between electron beam and sample several signals are generated, which can be measured by various detectors. These signals provide information from the topography, the chemical composition and the microstructure.
Technical data:
Field Emitter SEM
Resolution: 0.9 nm with 15 kV, 1.6 nm with 1 kV
Acceleration voltage: 200 V to 30 kV
Detector: SE, BSE, InBeamSE, InBeam BSE with energy filtering Beam Deceleration, Plasmacleaner
EDX and WDX system by Oxford Instrument
X-ray Diffractometer
X-ray diffractometry is used for the determination of the crystallographic structure of thin films, powders and bulk materials. At the department, two diffractometers of type Bruker AXS D8 Advance are available. These diffractometers consist of a source of radiation (copper X-ray tubes), monochromators, various slits and detectors. During the measurement the sample is irradiated with monochromatic X-rays and the diffraction at the crystal lattice is investigated. By scanning a pre-defined range of diffraction angles maxima in the reflected X-ray intensity can be determined being characteristic for each crystalline material. This consequently enables the determination of the phase composition of solid samples. The detectors available at the department are energy-dispersive, which results in an excellent signal-to-noise ratio, especially for steel samples, which tend to fluoresce under copper radiation. A Eulerian cradle allows to tilt the investigated sample thus making stress and texture analyses feasible. A high-temperature chamber (Anton Paar 1200 N) provides the possibility to heat samples up to 1200 °C in vacuum, air and oxidizing atmospheres enabling the investigation of phase transformations and chemical reactions.
Technical data:
- Measurement geometry: Bragg-Brentano, parallel beam, gracing incidence, transmission, reflection
- Radiation: copper K-alpha, line and point focus
- Detectors: scintillation counter, energy dispersive detectors (0D and 1D mode)
- Sample holder: nine position sample changer, Eulerian cradle, capillary holder and high-temperature chamber (up to 1200 °C)
- Investigation atmospheres: vacuum, air and oxidative
- Software: ICDD pdf-database 2018 und EVA (phase analysis), TOPAS (quantitative determination of phase compositions, Rietveld), TEXTURE (texture determination), LEPTOS (calculation of residual stresses)
Microscopy – Failure analysis
To clarify failure claims mostly photo-optical devices are used. For the macroscopic and microscopic assessment of failure claims stereomicroscopes and reflected-light microscopes, respectively, can be used by students during the tutorial failure analysis. All microscopes are equipped with a depth of focus correction.